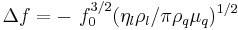Sauerbrey equation
The Sauerbrey equation was developed by G. Sauerbrey in 1959 as a method for correlating changes in the oscillation frequency of a piezoelectric crystal with the mass deposited on it. He simultaneously developed a method for measuring the characteristic frequency and its changes by using the crystal as the frequency determining component of an oscillator circuit. His method continues to be used as the primary tool in quartz crystal microbalance experiments for conversion of frequency to mass and is valid in nearly all applications.
The equation is derived by treating the deposited mass as though it were an extension of the thickness of the underlying quartz.[1] [2] Because of this, the mass to frequency correlation (As determined by Sauerbrey’s equation) is largely independent of electrode geometry. This has the benefit of allowing mass determination without calibration, making the set-up desirable from a cost and time investment standpoint.
The Sauerbrey equation is defined as:
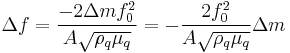 .
.
Equation 1 – Sauerbrey’s equation
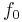 – Resonant frequency (Hz)
– Resonant frequency (Hz)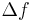 – Frequency change (Hz)
– Frequency change (Hz)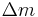 – Mass change (g)
– Mass change (g)- A – Piezoelectrically active crystal area (Area between electrodes, cm2)
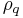 – Density of quartz (
– Density of quartz (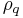 = 2.648 g/cm3)
= 2.648 g/cm3)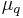 – Shear modulus of quartz for AT-cut crystal (
– Shear modulus of quartz for AT-cut crystal (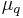 = 2.947x1011 g/cm.s2)
= 2.947x1011 g/cm.s2)
Because the film is treated as an extension of thickness, Sauerbrey’s equation only applies to systems in which the following three conditions are met: the deposited mass must be rigid, the deposited mass must be distributed evenly and the frequency change 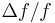 < 0.02.[3]
< 0.02.[3]
If the change in frequency is greater than 2%, that is, 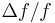 > 0.02, the Z-match method must be used to determine the change in mass.[2] The formula for the Z-match method is:[2]
> 0.02, the Z-match method must be used to determine the change in mass.[2] The formula for the Z-match method is:[2]
Equation 2 – Z-match method
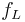 – Frequency of loaded crystal (Hz)
– Frequency of loaded crystal (Hz)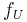 – Frequency of unloaded crystal, i.e. Resonant frequency (Hz)
– Frequency of unloaded crystal, i.e. Resonant frequency (Hz)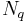 – Frequency constant for AT-cut quartz crystal (1.668x1013Hz.Å)
– Frequency constant for AT-cut quartz crystal (1.668x1013Hz.Å)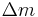 – Mass change (g)
– Mass change (g)- A – Piezoelectrically active crystal area (Area between electrodes, cm2)
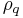 – Density of quartz (
– Density of quartz (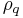 = 2.648 g/cm3)
= 2.648 g/cm3)- Z –
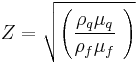
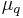 – Shear modulus of quartz (
– Shear modulus of quartz (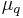 = 2.947x1011 g/cm.s2)
= 2.947x1011 g/cm.s2)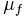 - Shear modulus of film (Varies: units are g/cm.s2)
- Shear modulus of film (Varies: units are g/cm.s2)
Limitations
The Sauerbrey equation was developed for oscillation in air and only applies to rigid masses attached to the crystal. It has been shown that quartz crystal microbalance measurements can be performed in liquid, in which case a viscosity related decrease in the resonant frequency will be observed:
where 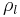 is the density of the liquid and
is the density of the liquid and 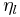 is the viscosity of the liquid (Kanazawa and Gordon 1985).
is the viscosity of the liquid (Kanazawa and Gordon 1985).
References
- ^ Sauerbrey, Günter (April 1959), "Verwendung von Schwingquarzen zur Wägung dünner Schichten und zur Mikrowägung", Zeitschrift für Physik 155 (2): 206–222, Bibcode 1959ZPhy..155..206S, doi:10.1007/BF01337937
- ^ a b c QCM100 – Quartz Crystal Microbalance Theory and Calibration, Stanford Research Systems.
- ^ A. K. Srivastava and P. Sakthivel, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 19(1), Jan/Feb 2001
Further reading
- K.K. Kanazawa and J.G. Gordon, Analytical Chemistry, 57(1985) 1770-1771
![\frac{\Delta m}{A}\ = \frac{N_q \rho_q}{\pi Z f_L}\tan^{-1} \left [ Z\tan \left ( \pi \frac{f_U-f_L}{f_U} \right ) \right ]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/2079feaaa13a5009469d5807051ef91f.png)